Abstract
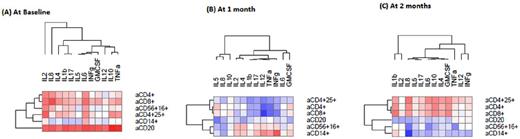
Umbilical cord blood transplantation (UCBT) is an alternative stem cell source for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The frequency of acute graft-versus-host-disease (aGvHD) in UCBT recipients is less than expected in recipients of adult donor allografts but delayed aGvHD can develop. Moreover, UCBT results in delayed and insufficient immune reconstitution leading to infection-related morbidity and mortality. We reasoned that an approach that would allow risk assessment for development of GvHD and/or for impaired immune reconstitution would be highly beneficial in adult UCBT recipients because it would guide therapeutic decisions for the prevention of these complications. Because reconstitution of hematopoietic lineages is delayed in UCB recipients, we focused on cytokines that can be assessed in patients' plasma at any time point before or after UCBT. Increase of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1b and TNF-α after BMT has been associated previously with the pathogenesis of GvHD. We previously determined that levels of IL-7 were inversely correlated with reconstitution of T cell subsets but were also associated with non-relapse mortality, development of GvHD and worse overall survival. In the present study, we employed a novel approach, which allows simultaneous assessment of multiple cytokines in a very small volume of patient's serum or plasma, to assess the prognostic value of this multi-cytokine profile in adult UCBT recipients. 32 patients with a median age of 50 years with hematopoietic malignancies were treated with reduced intensity conditioning (Flu/Mel/rATG) followed by two sequential UCB graft transplantation (dUCBT) and GvHD prophylaxis with tacrolimus and sirolimus. Results are based on 27 evaluable patients. Assessments were done prior to transplantation and at 1, 2, 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after dUCBT. Quantification of cytokines IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IFN-γ, TNF-α and GM-CSF in serum samples was conducted using the LUNARISTM Human 11-Plex Cytokine Biochip384 from AYOXXA Biosystems. Briefly, after diluting as 1:2 using the respective assay diluent, 5µl of samples or assay standards were loaded in duplicates on the AYOXXA Biochip and the assay was performed according to the manufacturers' instructions. Readout was performed using the AYOXXA Reader AR01 (Cat. No. LRS-001, AYOXXA Biosystems) and data were analyzed using the LUNARISTM Analysis Suite Software (Cat. No. LAS-001, AYOXXA Biosystems). Based on their median levels, cytokines could be categorized in four patterns of kinetics in comparison to pre-transplant baseline values: 1) Without significant changes (IL-2); 2) decrease over time (IL-1b, IL-17); 3) increase at 1-month after dUCBT and subsequent decline (IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-α, GM-CSF); 4) increase at 2 months after UCBT and subsequent decline (IFN-γ). At baseline, most cytokines correlated with total lymphocytes, CD4+, CD8+ subsets, CD4+CD25+ Treg, CD56+CD16+ NK cells, CD20+ B cells and CD14+ monocytes. At 1-month after dUCBT, the correlations with immune cell types disappeared for most cytokines and only CD14+ monocytes correlated with IFN-γ. At 2-months after dUCBT, most cytokines were positively correlated with T cell subsets. IL-8 displayed a unique pattern of correlation with CD14+ monocytes and B cells, both of which have potent antigen presenting function. Specifically, at 2-months after dUCBT IL-8 inversely correlated with CD14+ cells (r=-0.71, p=0.0007) and this pattern persisted until day 100, when CD20+ cells also showed a significant inverse correlation with IL-8 (r=-0.56, p=0.006). These inverse correlations declined by 6 months after dUCBT. IL-8 levels after BMT were previously associated with infectious complications, which subsequently drive elevation of IL-6 and development of GvHD. Our findings pose the intriguing possibility that multicytokine profile analysis might serve as a biomarker to guide patient management such as work-up for infectious complications that might prevent GVHD development in dUCBT recipients. Analysis of correlations between multicytokine profile and such clinical outcomes is currently ongoing. Our results provide evidence for the feasibility of a novel method for multicytokine assessment in patients' plasma, which might guide patient management, to diminish complications after dUCBT.
Antin: Gentium SpA/Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal